|
|
| This glossary uses network terms from the OSI model. Click on one of the categories on the left or on the image below. Click the View All link to see all terms. Use the alphabet to jump to that letter. Some of the terms could be used on multiple layers, but they are grouped in the most common layer. |
Data Link
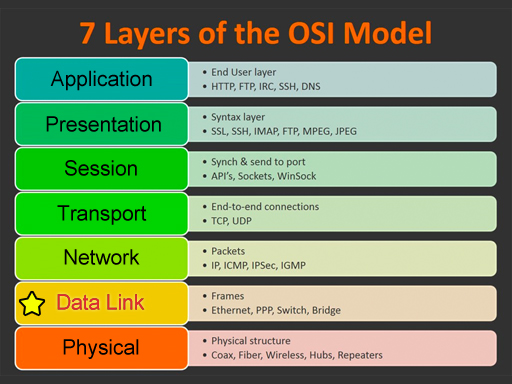
View All
|
|
|
#
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
M
N
O
P
Q
R
S
T
U
V
W
X
Y
Z
|
#
802.11 |
| The IEEE standard for wireless LAN (WLAN) implementation. The IEEE 802.11 standard includes a number of notable specifications including 802.11a: 54Mbps maximum speed, 5GHz UNII frequency range; 802.11b: 11Mbps, 2.4GHz ISM frequency range; 802.11g: 54Mbps, 2.4GHz; 802.11n: 600Mbps, 2.4GHz and 5GHz; 802.11ac: 1300Mbps, 5GHz. (Data Link Layer) Top |
|
|
802.1X |
| A port-based authentication protocol used on wired and wireless LAN access devices. The IEEE 802.1X standard is employed on Layer-2 switches and wireless access points (WAP) to require systems connected to interfaces on such devices to submit credentials—username and password, for instance—before network access is granted. (Data Link Layer) Top |
|
|
A
Asynchronous communication |
| A data communication method between two devices that is achieved without using a common clock signal. Other characteristics of asynchronous communication include periods of no communication at all and the ability to vary the rate of bit transmission. The classic RS-232 serial port included with most legacy computer systems is a well-known interface that employs asynchronous communication. (Data Link Layer) Top |
|
|
B
Bandwidth |
| In analog or digital communication, the channel occupied by the carrier and measured as the difference in hertz (Hz) between the highest and lowest frequencies in the channel. (Data Link Layer) Top |
|
|
Biometrics |
| A form of identification based on individual human traits. Literally “the measure of life,” the field of biometrics uses a variety of biological measurements in an attempt to differentiate one human from all others by using features such as fingerprints, palm prints, voice, handwriting, retina, iris and recognition of facial features. (Data Link Layer) Top |
|
|
Bridge |
| In Ethernet, a Layer-2 legacy networking device replaced almost completely by routers in modern networks. Bridges replaced Layer-1 repeaters for interconnecting separate network cable segments and featured the advantage of understanding MAC addresses and Ethernet frame boundaries, allowing for the ability to forward data, when appropriate, and block—or filter—data that is not meant for a different segment. Today, the industry uses the term bridge as a verb to refer to passing information transparently from one interface to another on the same device without that device being a destination or source during the transmission. (Data Link Layer) Top |
|
|
C
Checksum |
| An error detection mechanism for data that is based on the data but is generally much smaller than the original data. The best checksum algorithms result in the generation of a substantially different checksum after a relatively small change in the data. Most checksums are used to discover undesired changes in the original data, but longer checksums can even be used to recover the original data that was changed. (Data Link Layer) Top |
|
|
D
Data |
| Any form of information that is used as input to a system or application for processing or that is produced as the output from a system or application. After the better part of a century of electronic data processing, data collection and analysis has entered an arena known as “big data.” The term big data analytics speaks to the capacity of modern computers to scour such vast quantities of complex and largely unrelated data sets and find exploitable connections and produce useful insights into a deeper meaning in a reasonable amount of time. (Data Link Layer) Top |
|
|
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) |
| A TCP/IP protocol for assigning IP addresses and related settings to clients on a temporary or permanent basis. Windows clients are set to seek a lease from a DHCP server by selecting “Obtain an IP Address Automatically” in a network adapter’s IP properties dialog. As an alternative, technicians or users can enter static IP settings that do not change until manually altered. (Data Link Layer) Top |
|
|
Driver |
| Software code that allows an operating system to use a piece of hardware by providing logical control. Operating systems are not natively capable of accessing hardware. Drivers specific to both the operating system and the hardware to be controlled act as translators between the two, accepting instructions from the operating system and producing instructions for the hardware and interrupt signals for the BIOS, which is responsible for physical control of the interfaces that lead to the hardware being controlled. (Data Link Layer) Top |
|
|
E
Encapsulation |
| The addition of control information to a data payload to form a protocol data unit (PDU) that is compatible with the encapsulating technology. Encapsulation is used as a technique for migration from the use of one protocol to a replacement protocol at the same layer, such as from IPv4 to IPv6. It can also be used as a security mechanism to obscure a PDU within another of the same type. (Data Link Layer) Top |
|
|
Ethernet |
| The most common LAN technology in use today. Ethernet, as a Layer-2 protocol, communicates directly with adjacent Layer-3 protocols, such as IP, as well as with the Layer-1 interface electronics that attach to networking media and encode the digital signals passed from above. (Data Link Layer) Top |
|
|
F
Frame |
| The basic data unit of Layer-2 and some Layer-1 protocols. As a protocol data unit (PDU), a frame is essentially one step above a bit. In fact, a frame is the first data structure above the bit level that gathers bits into a standardized format that is based on the protocol in question. (Data Link Layer) Top |
|
|
I
Interface |
| A physical port used for connectivity to a network or peripheral device; a point of interconnection between two cables, two components, two protocols, two software processes, or two networks. Cabling interfaces are often interchangeably referred to as ports. Interfaces between software or protocol objects can also be referred to as ports in a logical sense. The term socket is also used in some cases with the same meaning. (Data Link Layer) Top |
|
|
J
Jitter |
| Variation in the latency (delay) on a network. Although delay can be tolerated in real-time connections at significant levels, a small amount of jitter can greatly disrupt such a connection. Proper buffering can mitigate the effects of reasonable jitter, but considerable jitter will underrun the buffer and cause degradation. (Data Link Layer) Top |
|
|
L
Latency |
| The amount of delay in a communication pathway. For non-real time traffic, latency is not a concern until the delay is so extensive that the application responsible for the data transmitted fails as it waits for a response from the opposing end. With real-time traffic, latency has a more noticeable effect. Nevertheless, users generally do not perceive a roundtrip latency less than 250ms in VoIP networks. (Data Link Layer) Top |
|
|
M
Man-in-the-Middle Attack (MITM) |
| Any of a family of cyber-attacks characterized by insinuating the attacking system between two legitimately communicating systems. MITM attacks can be perpetrated to steal information or influence the flow of information. Attackers can eavesdrop passively or masquerade as one or both compromised endpoints. (Data Link Layer) Top |
|
|
Mirroring |
| Configuring an interface on an Ethernet switch to forward frames intended for all other interfaces. Normally, Layer-2 Ethernet switches will forward only unknown traffic and traffic intended for the device attached to a particular port. (Data Link Layer) Top |
|
|
P
PPP |
| Stands for "Point-to-Point Protocol." PPP is a protocol that enables communication and data transfer between two points or "nodes." For many years, PPP was the standard way to establish a dial-up connection to an ISPs. As dial-up modems were superseded by broadband devices, PPP connections became increasing. However, PPP lives on in "PPP over Ethernet" (PPPoE), which is a common way to connect to the Internet using a DSL modem. (Data Link Layer) Top |
|
|
S
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) |
| A bridging and switching protocol designed to prevent broadcast storms in logical segments that contain physical loops. (Data Link Layer) Top |
|
|
Switch |
| A Layer-2 device that forwards, filters, or floods frames based on the destination address in the header of the frame. Ethernet switches maintain a table that consists of the physical interfaces on the switch associated with the MAC addresses that have been learned by the switch through inspection of the source addresses in the headers received on the associated ports. Switches are not authorized to discard unknown traffic and must therefore flood it. (Data Link Layer) Top |
|
|
C
Vable modem |
| The customer premise equipment (CPE) used to send and receive internet traffic over a coaxial cable television circuit. Cable modems use a technology known as DOCSIS (Data Over Cable Service Interface Specification) to encode the data traffic for transmission onto the broadband cable TV network and decode such signals as they are received. (Data Link Layer) Top |
|
|
V
Virtual LAN (VLAN) |
| A broadcast domain created through configuration on a Layer-2 switch. All interfaces on the switch that are placed in the same VLAN are part of the same broadcast domain. A router is required to allow communication from one broadcast domain to another. The value of VLANs stems from the ability to create security domains separated by routers without the need to position devices together in the same area of the enterprise. (Data Link Layer) Top |
|
|
Virtual Private Network (VPN) |
| A network created by encrypting traffic between two endpoints that are connected to one another across an insecure network, such as the internet. Security and tunneling protocols, including IPsec and L2TP, are used to create a secure channel for all traffic to traverse. VPNs can also be created higher in the protocol stack using SSL and TLS. (Data Link Layer) Top |
|
|
W
Wide Area Network (WAN) |
| A network that is leased from a service provider; a network that geographically spans a large area, such as between cities or around the world; a network spanning a great distance between two router interfaces; a network that uses a class of Layer-2 protocols positioned for deployment on a WAN. Technically, WAN and internetwork are not interchangeable terms, but many in the industry, including experts, seem to believe that they are. WAN links have a recurring fee that must be paid under pain of cancellation. (Data Link Layer) Top |
|
|
Wireless security |
| A group of protocols that are used for authentication and to secure wireless LANs (WLANs) to varying levels. Security for WLANs also includes not broadcasting the SSID, or name of the network, and keeping a list of MAC addresses to filter based on allowed or denied wireless supplicants. (Data Link Layer) Top |
|
|