|
|
| This glossary uses network terms from the OSI model. Click on one of the categories on the left or on the image below. Click the View All link to see all terms. Use the alphabet to jump to that letter. Some of the terms could be used on multiple layers, but they are grouped in the most common layer. |
Physical
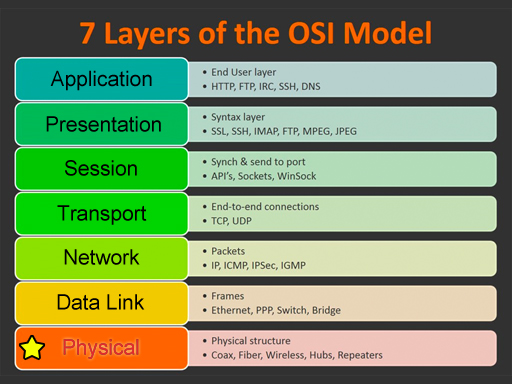
View All
|
|
|
#
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
M
N
O
P
Q
R
S
T
U
V
W
X
Y
Z
|
#
3G |
| The second generation of digital cellular communications technology characterized by minimum speeds of hundreds of kbps and tens of Mbps at the high end. Providers of 3G service continue to use circuit switching—as was done in the early voice-only 2G technologies—to make voice calls. (Physical Layer) Top |
|
|
4G |
| A digital cellular communications technology that ranges in speed from 100Mbps to 1Gbps and is based entirely on a packet-switched IP network. With 4G networks, voice is implemented as voice over IP (VoIP). (Physical Layer) Top |
|
|
5G |
| An emerging digital cellular communications technology exceeding the specifications of earlier generations of mobile communication. As of early 2017, the final touches had not been agreed upon by the International Telecommunication Union (Physical Layer) Top |
|
|
A
Analog signal |
| A communications waveform that is analogous to the source of the signal. Often represented as a sine wave, analog signals must be transmitted all the way to the target exactly as produced in order to provide a precise representation at the receiving end. Due to attenuation and external noise influence, this goal is largely unattainable. Filters and shields can be implemented with analog signals to somewhat improve the quality of the received signal. (Physical Layer) Top |
|
|
Antenna |
| A device that converts between radio waves and electrical current. Antennas are used in various circuits and systems to transmit and receive wireless signals in the form of radio frequency energy. (Physical Layer) Top |
|
|
Attenuation |
| Loss of signal strength along a communications pathway. Attenuation is often measured in decibels (dB) and results from natural resistance in the wired or wireless channel and from other environmental factors. (Physical Layer) Top |
|
|
B
Backbone |
| A media pathway of higher capacity than those used to connect end devices to the network. Backbones are often deployed to interconnect equipment rooms or cross-connection spaces containing concentrating devices used to offer connectivity to end devices in a star-wired infrastructure. Backbones simultaneously carry traffic for multiple end devices. (Physical Layer) Top |
|
|
Baseband |
| A type of digital signaling that features the use of a single frequency or near-zero bandwidth to transmit a bitstream. Baseband signaling is used in Ethernet networks and is represented by “BASE” in the names of the various physical-layer technologies, such as 10BASE-T, 100BASE-TX, 1000BASE-T and 10GBASE-T. (Physical Layer) Top |
|
|
Binary |
| Characterized by having two parts. A binary system is one that has two separate components. In electronics, binary can refer to the state of a circuit or memory cell, either on or off, present or not, “yes” or “no.” Scientists use the binary numbering system to mathematically represent and predict such circuits with two numerals—0 and 1—allowing for the creation and troubleshooting of individual components as well as entire systems. Popular usage of the term refers to the binary numbering system, which is one of only a few such systems (out of an infinite possibility of numbering systems) that humans commonly employ to describe the world around them. Octal (base-8), decimal (base-10) and hexadecimal (base-16) are the other three numbering systems that you can expect to deal with in the technology industry. (Physical Layer) Top |
|
|
Bit (b) |
| The basic unit of the binary numbering system. The word bit is a portmanteau of the term “binary digit.” Therefore, the word bit refers to one of the two numerals, 0 or 1, in the binary numbering system. The industry also supports using the word “bit” to represent a single position in a numeric value that is being expressed in binary, regardless of its bit-value. (Physical Layer) Top |
|
|
Bits per second (b/s or bps) |
| A unit of measure for the movement of data between devices and/or across a medium. Also known as “bitrate.” Almost all measures of data transmission speed are based on bps. (Physical Layer) Top |
|
|
Broadband |
| A type of wide-bandwidth communications signaling that supports the transmission of data from multiple sources, including those of varying types, separated across the series of frequencies in the bandwidth. (Physical Layer) Top |
|
|
Byte (B) |
| The most basic collection of bits required by a transmission pathway. Earlier systems required eight bits be transmitted or operated upon simultaneously, so the legacy definition of bytes containing exactly eight bits endures today. However, it is correct to say that an x86-64 processor operates upon a 64-bit byte, which might confuse the vast preponderance of the technology community. It has become common to use the term “octet” to refer to a group of eight bits because it is impossible to dispute that the root of the word refers to the value eight. (Physical Layer) Top |
|
|
C
Channel Service Unit/Data Service Unit (CSU/DSU) |
| A data circuit-terminating equipment (DCE) form of customer premise equipment (CPE) used to connect enterprise networking devices to a synchronous digital network, such as a T1 circuit. (Physical Layer) Top |
|
|
Cloud |
| A term stemming from the abstract concept that the same data and services are available from seemingly limitless points of access. Cloud computing is a potentially extensive infrastructure of such services and methods of access, whether supplied by a cloud provider or internally, as from an enterprise’s own data center. (Physical Layer) Top |
|
|
Coaxial cable |
| Also known as coax for short; a common form of copper cabling characterized by having two conductors: one being the core of the cable, which is surrounded by the other, a braided shield. This design results in the inner and outer conductors having a common axis of rotation, which creates a signal pathway that supports higher frequencies with less signal loss and with less susceptibility to outside interference. (Physical Layer) Top |
|
|
D
DSL (Digital Subscriber Line) |
| A broadband internet-access circuit based on a standard pair of phone wires. (Physical Layer) Top |
|
|
F
Fiber |
| Fiber optics, or optical fiber, refers to the medium and the technology associated with the transmission of information as light pulses along a glass or plastic strand or fiber. Fiber optics is used long-distance and high-performance data networking. (Physical Layer) Top |
|
|
G
GPS (Global Positioning System) |
| Developed for military use, the worldwide network of satellites used to pinpoint the location and altitude of terrestrial mobile electronics; in general, the access service subscribed to or the devices employed by users of the GPS network. GPS transceivers are built into devices from smartphones and wearable fitness devices to the electronic consoles of land-, air-, and water-faring vehicles, many of which also provide entertainment functions. In addition to location, mapping, and navigation services, GPS is used by receivers for clock synchronization because of the precise atomic clocks that are present in the satellites. (Physical Layer) Top |
|
|
H
Hub |
| A Layer-1 Ethernet device with multiple network interfaces; in general, the central concentrating device in a star-wired hub-and-spoke topology. The Ethernet hub is essentially a multiport repeater dealing only with regenerating inbound signals before sending them out all ports simultaneously. As the generic center of a star-wired topology, the hub device can be a hub, switch, concentrator, router, or a multifunction device offering a combination of such functions. (Physical Layer) Top |
|
|
I
ISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network) |
| A collection of lower-layer protocols and related circuits often used for broadband internet access. ISDN is named for its all-digital support of voice, data, and video services. (Physical Layer) Top |
|
|
L
LAN (Local Area Network) |
| A network that is fully owned by an enterprise; a network that geographically spans a small area, such as a building or floor; a network consisting of all devices behind and including a single router interface; a network that uses a class of Layer-2 protocols limited to deployment on a LAN. (Physical Layer) Top |
|
|
M
Modem (modulator/demodulator) |
| A data communications equipment (DCE) device that assists a data terminal equipment (DTE) device, such as a personal computer, in communicating across a wide-area link. (Physical Layer) Top |
|
|
N
Node |
| Any active device anywhere in a network. Node is a generic term that comes in handy whenever the speaker or writer needs a term that does not commit to a function. On occasion, “node” is used in place of the term host as an adjective to mean “related to one of the devices on an IP network,” as in “node ID” in place of “host ID.” (Physical Layer) Top |
|
|
O
Optical fiber |
| A type of cabling media that guides light waves down a core made of glass or plastic. Fiber optic cable is categorized into two primary types: multimode (MMF) and single-mode (SMF). MMF is used primarily for LAN implementations, where distances are shorter than those found in the wide area, an application best suited for SMF. (Physical Layer) Top |
|
|
T
T1 (also written T-1) |
| One of a class of digital terrestrial circuits that consists of 24 distinct time-division multiplexed channels and a bitrate of 1.544Mbps. The T1 circuit carries a signal known as Digital Signal Level 1 (DS-1). Each of the 24 channels consists of a 64kbps signal known as a DS-0. T1s, in turn, are gathered into groups of 28 to form a DS-3 signal that is transmitted over a T3 circuit at a rate of 44.736Mbps. T1 circuits were once extremely popular dedicated leased telco lines because dedicated bandwidth results in a much better sustained performance when compared to shared circuits of considerably greater bandwidth. (Physical Layer) Top |
|
|
Transceiver |
| A portmanteau for transmitter/receiver that refers to a circuit that transmits outbound traffic to and receives inbound traffic from a network. Transceivers also act as converters that turn the type of digital signal in the computer and network card into the type of digital signal that is compatible with the network media. (Physical Layer) Top |
|
|
Twisted-pair cable |
| The primary form of copper cable used in modern star-wired networks. Unshielded twisted-pair (UTP) is the wiring standard recommended for structured cabling installations. (Physical Layer) Top |
|
|
W
Wavelength |
| The property of analog and digital signals found by measuring the distance between where one wave begins and where the subsequent wave begins. Wavelength is inversely proportional to frequency, which is the measure of time that it takes for one wave to complete but is calculated as the number of waves that are transmitted in the space of one second. Therefore, if more waves can be transmitted per unit of time (higher frequency), then the distance spanned by each wave must be less (shorter wavelength). (Physical Layer) Top |
|
|
Wi-Fi |
| The term used by the Wi-Fi Alliance to refer to the technology that the IEEE calls 802.11. There are five protocols in the Wi-Fi family that have enjoyed a respectable amount of support: 802.11a, 802.11b, 802.11g, 802.11n, and 802.11ac. (Physical Layer) Top |
|
|
Wireless Access Point (WAP) |
| A concentrating device for wireless networks. WAPs create a wireless infrastructure and often provide connectivity to the wired infrastructure as well. Because both wired and wireless clients share the same IP subnet, the WAP plays the role of translational bridge (xBr), converting between 802.11 and 802.3 media access methods and frame formats. Providing routing functionality in the same situation would work for the protocol conversion but not for keeping all clients on the same subnet. (Physical Layer) Top |
|
|
Wireless |
| A form of node connectivity that replaces cables with radio waves or invisible wavelengths of light. (Physical Layer) Top |
|
|